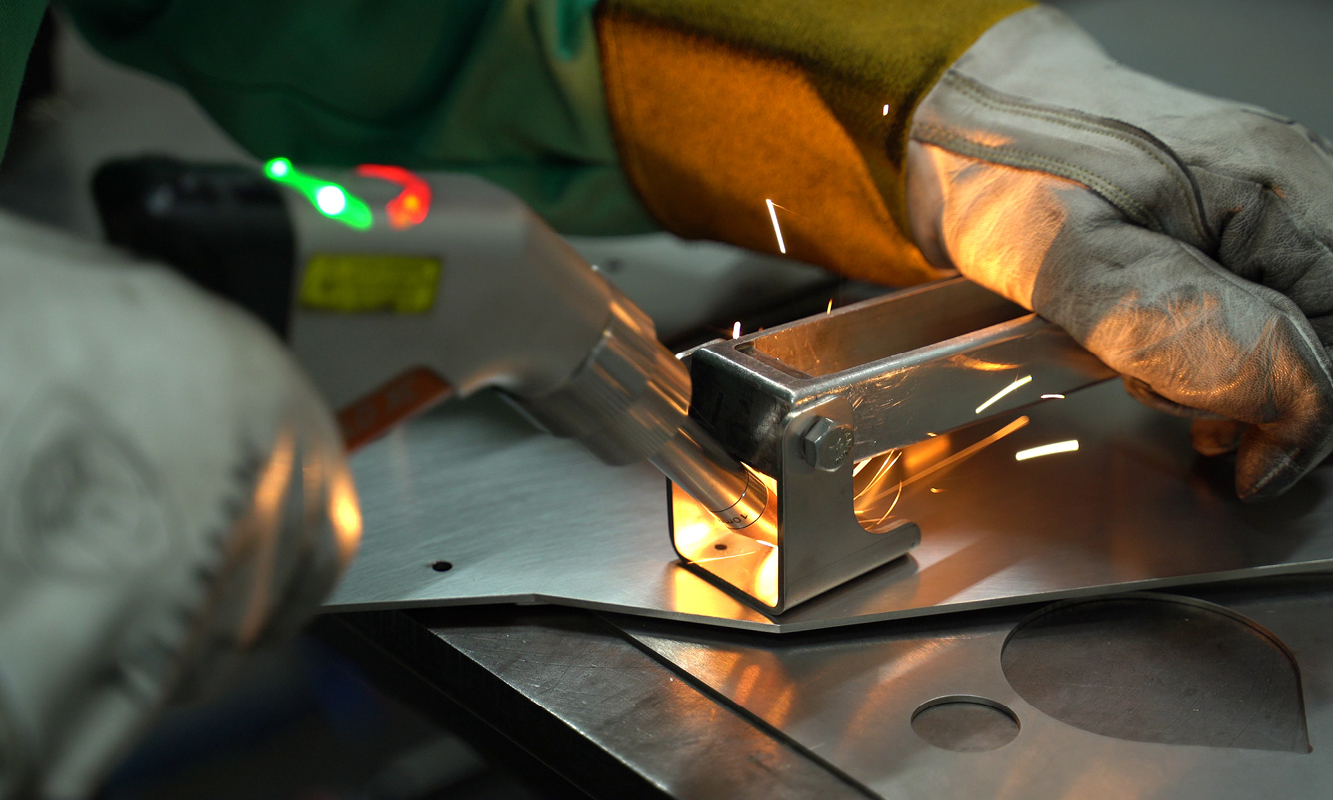
Laser welding is becoming a go-to option in many shops. But with its high energy output comes unique safety considerations.
The same focused beam that makes laser welding so effective can also pose risks—like harmful radiation, fumes, and even electrical hazards. That’s why having the right tools and safety protocols in place is important for any shop owner or fabricator.
In this article, we’ll cover the key safety measures every laser welding operation should follow. We will also touch on how newer technologies, like cobot laser welding, can help you maintain a safer, more efficient shop.
In this article:
• Understanding the Hazards ›
• Creating a Safe Environment ›
• Personal Protective Equipment for Laser Welding ›
• Training and Education for Laser Welding Safety ›
• Safety Standards and Regulations to Follow ›
• Why Cobot Laser Welding Offers Enhanced Safety Compared to Manual, Hand-Held Welding ›
• Ensuring Safety in Every Weld ›
Understanding the Hazards
Laser welding presents unique safety hazards that shop owners and fabricators need to be aware of. Here are the main risks involved:
• Laser radiation: One of the most significant dangers comes from the laser radiation itself. The high-energy beams can cause severe eye and skin injuries, even from scattered reflections. A major concern is that laser light is often invisible, making it easy to underestimate its risk. Without proper precautions, operators may not realize they’re in danger until it’s too late.
• Fume and gas exposure: Laser welding can produce harmful fumes and gases, depending on the materials being welded. These fumes may contain toxic substances like chromium, nickel, or zinc, which pose severe health risks if inhaled. Proper ventilation and fume extraction systems are needed to protect your team from respiratory hazards.
• Electrical hazards: High-voltage equipment introduces the risk of electrical shocks. Faulty wiring, equipment malfunctions, or improper handling can lead to serious or even fatal injuries. Regular maintenance and inspection of all electrical components are essential to minimize these risks.
• Fire risks: Laser welding generates intense heat, which can ignite flammable materials in the welding area. Without careful control of the environment and proper safety measures, such as fire-resistant barriers and extinguishers, even a small spark can turn into a dangerous fire hazard.
Creating a Safe Environment
To prevent accidents and injuries, you need to establish a safe environment for your laser welder. You can reduce the risks associated with laser welding if you create a designated controlled area, use proper safety hardware, and leverage built-in safety features.
Designated Laser Welding Controlled Area
A designated laser-controlled area is essential for preventing accidental exposure to laser beams. This area should be light-tight, meaning no laser light can escape, to ensure that both direct and scattered beams are contained. This reduces the risk of eye and skin injuries for anyone nearby.

Proper signage is also important. Signs should clearly indicate the presence of laser hazards and remind everyone entering the area to follow safety protocols. This constant visual reminder ensures everyone in the vicinity remains aware of the potential dangers and takes the necessary precautions.
Weld Cell Safety Hardware
Safety interlocks connected to the laser welding power source are critical; these interlocks automatically shut down the system if unsafe conditions are detected, such as if a door is opened or a barrier is breached. This immediate response helps minimize the risk of accidents or injuries, providing an extra layer of protection for operators and other personnel.
Safety Features of Laser Welding Systems
Many laser welding systems come equipped with built-in safety features that enhance operational safety. For example, the IPG Handheld Laser Welder includes several key safety mechanisms:
• Key for Laser ON/Off: Prevents unauthorized use of the laser, ensuring only trained and authorized personnel can operate the system.
• 2-Step Laser Operation Trigger (Enable and Fire): Requires two distinct actions to activate the laser, reducing the risk of accidental firing.
• Part-Head Contact Safety Circuit: Ensures the laser only activates when in contact with the part to be welded, preventing accidental exposure to the laser beam.
These features, combined with a controlled environment and proper safety hardware, create a comprehensive approach to laser welding safety.
Personal Protective Equipment for Laser Welding
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) safeguards operators from the various hazards associated with laser welding. Proper PPE acts as the last line of defense against injuries, protecting workers from laser radiation, heat, and other risks.
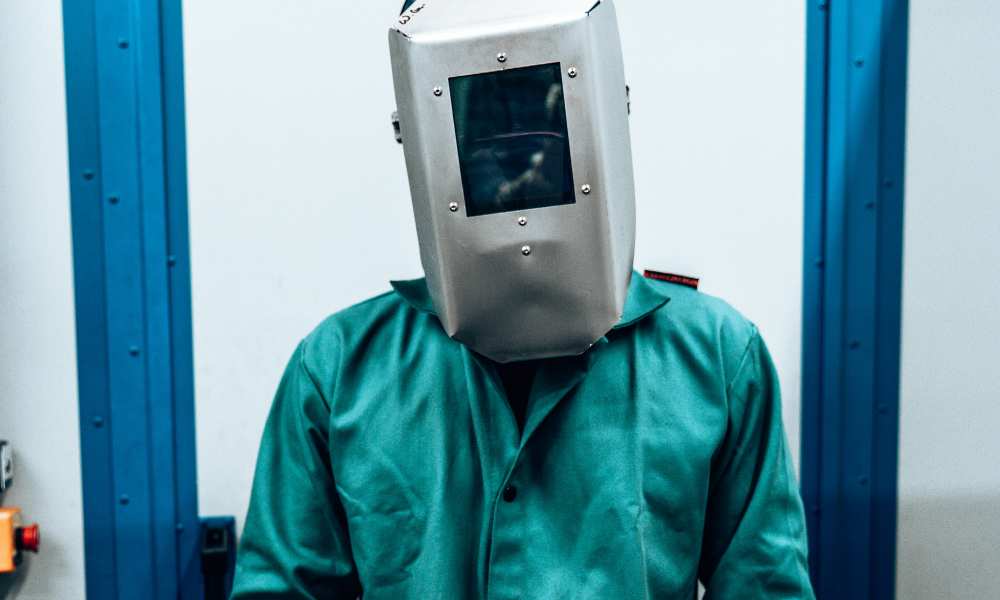

Types of PPE
• Laser-safe goggles: The most crucial piece of PPE for laser welding. These are specifically designed to protect the eyes from the intense and often invisible laser radiation. The goggles should be selected based on the wavelength and optical density (OD) requirements of the laser being used to ensure maximum protection.
• Helmet with laser radiation filter: This specialized welding helmet shields the face and head from laser radiation. This additional protection is especially important when working with high-powered lasers or in environments where reflected beams may be a concern.
• Gloves, long sleeves, and work boots: Standard welding PPE, such as heat-resistant gloves, flame-resistant long sleeves, and sturdy work boots, should always be worn. These items protect against burns, sparks, and hot metal spatter that are common in any welding environment.
Make sure all your operators are equipped with and trained to use the correct PPE. This will contribute to a safer workplace and demonstrates a commitment to safety.
Training and Education for Laser Welding Safety
Properly trained operators understand the risks involved and will follow safety protocols diligently, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
Importance of Training
Every operator involved in laser welding must receive comprehensive training. This training should cover all aspects of laser welding safety, including proper use of equipment, PPE requirements, handling emergency situations, and maintaining a safe workspace.
Training should also emphasize the invisible nature of laser radiation, the dangers of fume and gas exposure, and the risks of electrical hazards and fire. By understanding these risks, operators are better equipped to take appropriate precautions and respond quickly to any unsafe conditions.
Example: IPG LightWeld Training Requirement
For some laser welding systems, such as the IPG LightWeld, training is not just recommended—it’s mandatory. Before activation, the manufacturer requires operators to complete a specific training course that covers the system’s safety features and proper usage. Only after completing this course do operators receive a code to activate the laser welding power source.
This approach ensures that every operator is fully aware of the system’s safety protocols and is prepared to handle the equipment responsibly. Regular refresher courses and updates on safety protocols are also important to keep safety knowledge current.
Safety Standards and Regulations to Follow
Safety standards and regulations provide clear guidelines on how to manage and mitigate the risks associated with laser welding, ensuring a safer working environment for everyone involved.
Key Safety Standards
• ANSI Z136: Safe Use of Lasers
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Z136 standard outlines safety measures for the use of lasers in industrial settings. It provides guidelines on laser classification, hazard analysis, and the use of protective equipment. Following ANSI Z136 ensures that the appropriate safety protocols are in place to protect operators from laser radiation and other hazards.
• OSHA Guidelines for Laser Safety
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides laser safety guidelines to protect workers from the hazards associated with laser operations. These guidelines cover aspects such as exposure limits, safety controls, and employee training. Compliance with OSHA’s standards is not only a legal requirement but also a critical component of maintaining a safe workplace.
• ISO 11553: Safety of Machinery – Laser Processing Machines
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 11553 standard focuses on the safety of laser processing machines, including laser welding systems. This standard specifies safety requirements for the design, installation, and use of laser machines to minimize risks associated with laser radiation, electrical hazards, and mechanical hazards.
Why Cobot Laser Welding Offers Enhanced Safety Compared to Manual, Hand-Held Welding
While manual, hand-held laser welding can offer flexibility, it also comes with increased risks due to the proximity of operators to the laser beam and potential for human error.
Cobot laser welding provides a safer alternative by reducing direct human exposure and ensuring a higher level of control over the welding process.
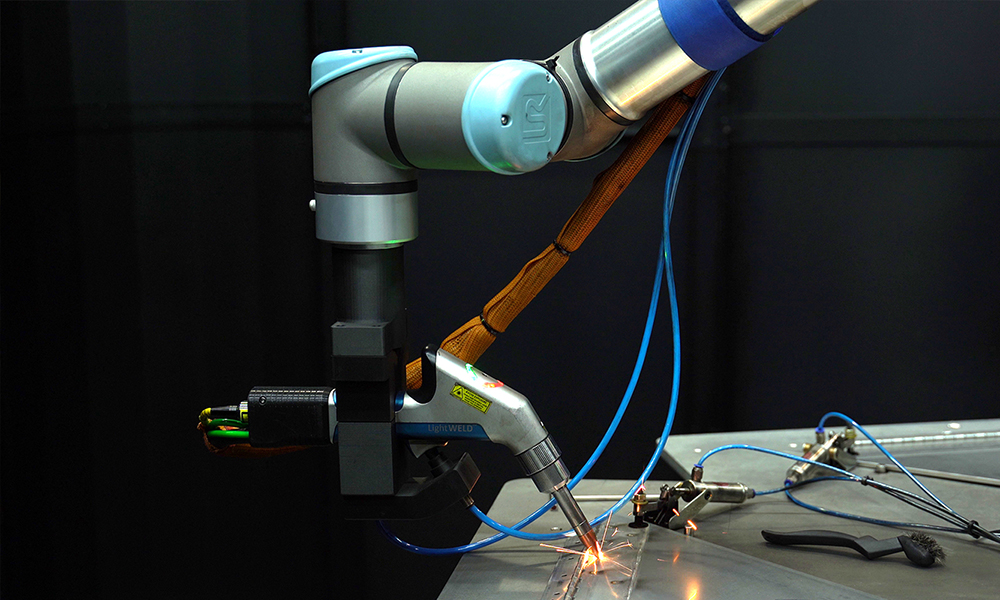
Benefits of Cobot Laser Welding
• Reduced human exposure: Using a Cobot (collaborative robots) keeps human operators at a safe distance from the laser beam, significantly lowering the risk of accidental exposure to harmful laser radiation.
• Consistent process control: Cobots excel in maintaining consistent process control. Unlike manual welding, where human error can lead to mistakes or safety lapses, cobots follow programmed safety protocols. This reduces the chances of accidents caused by operator fatigue, distraction, or lack of training.
• Integrated safety features: Modern cobot laser welding systems come equipped with advanced safety systems like interlocks, shields, and sensors. These built-in safety features provide multiple layers of protection:
– Interlocks ensure that the laser cannot operate unless all safety conditions are met, such as doors being closed or barriers in place.
– Shields and barriers prevent laser light from escaping the designated welding area.
– Sensors monitor the environment and automatically shut down the system if an unsafe condition is detected.
Cobot Systems’ Laser Welding Solutions
Cobot Systems’ laser welding cobot system incorporates these safety measures and more. Features like precise control over laser movement, customizable safety zones, and integrated monitoring systems provide real-time feedback on the welding process. This allows for continuous adjustments, ensuring optimal safety conditions throughout the welding operation.
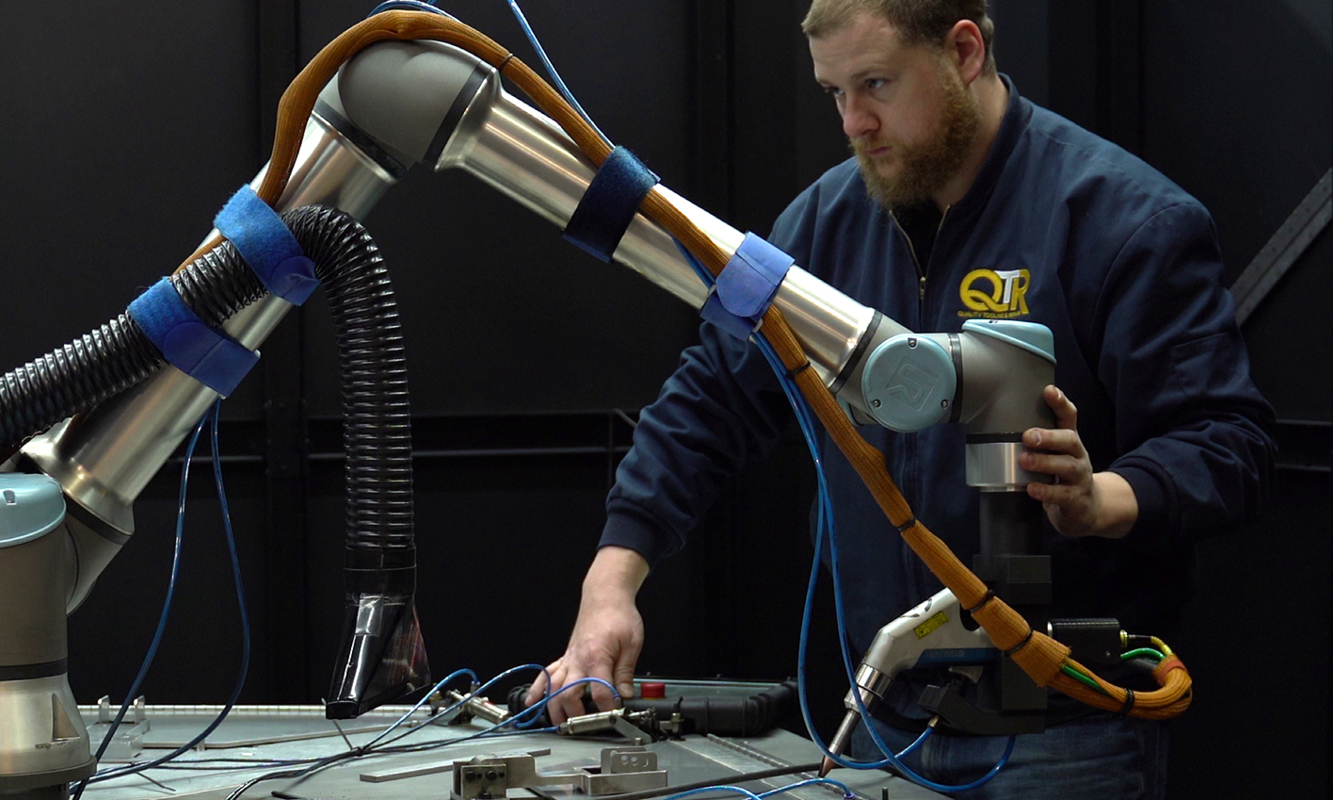

Ensuring Safety in Every Weld
Safety should always come first in laser welding. Following the right safety measures is key to protecting your team and keeping things running smoothly. By setting up controlled areas, using the proper PPE, and sticking to standards like ANSI, OSHA, and ISO, you can greatly reduce the risks that come with laser welding.
Cobot laser welding takes safety a step further by keeping operators away from the laser beam and ensuring that safety procedures are consistently followed.
Explore our laser welding cobot system today and see how they can improve your manufacturing processes. Speak with our experts or schedule a demo to find out how Cobot Systems can help you achieve a safer, more efficient shop environment. Make the switch to smarter, safer welding now.